



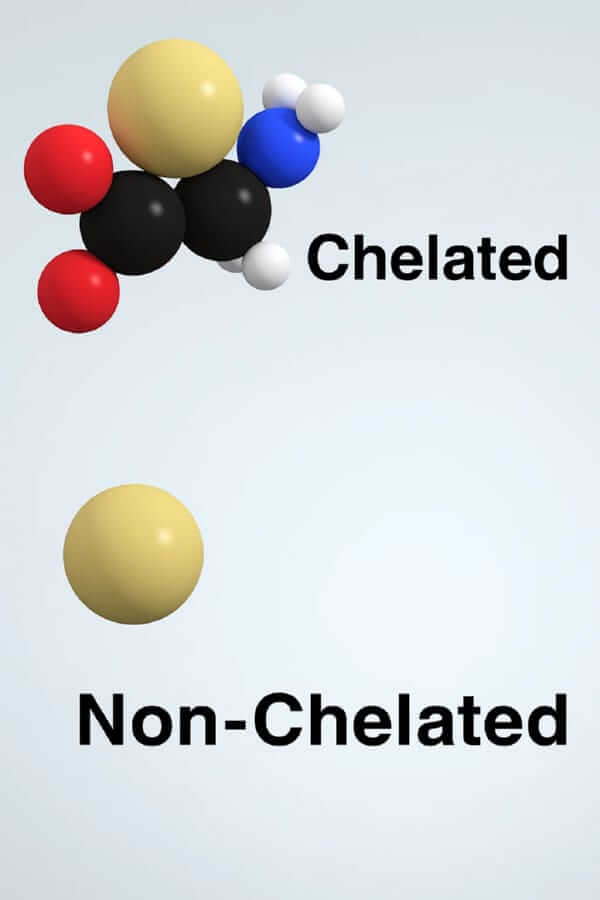
Chelated Minerals Explained: The Key to Better Absorption
Ever wonder why some mineral supplements, like magnesium or zinc, cause stomach upset or seem to have little effect? The secret isn't just what you take, but how it's delivered. What are chelated minerals, and why are they a game-changer for effective supplementation? The answer lies in a clever scientific process called chelation, which unlocks superior mineral absorption. For those who demand both effectiveness and comfort from their supplements, you can explore our line of advanced chelated minerals.
The Problem with Standard Mineral Supplements
Minerals are essential for our health, but in their raw, inorganic form, our bodies struggle to absorb them. Many common supplements use simple mineral salts like magnesium oxide or zinc sulfate. These forms present a few key challenges inside our digestive system.
The Charge and Competition Problem in Your Gut
Inorganic minerals carry a positive electrical charge. This causes them to compete with other similarly charged minerals for absorption in the gut. Furthermore, they can bind with other compounds in your food (like phytates), forming large, insoluble complexes that your body simply can't absorb.
Why Forms like Oxides Have Low Bioavailability
This competition and binding lead to very low mineral bioavailability. For example, some studies suggest that as little as 4% of the magnesium from magnesium oxide is actually absorbed. The rest is simply wasted, passing through your system without providing any benefit.
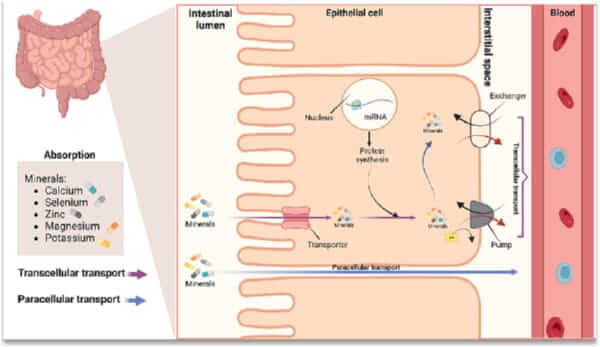
The Link Between Poor Absorption and Digestive Issues
That unabsorbed mineral content sitting in your intestines is often the culprit behind stomach upset and the laxative effect associated with some supplements. It's not the mineral itself causing the problem, but the body's inability to properly absorb it.
What Are Chelated Minerals? A Simple Analogy
So, why are chelated minerals better? "Chelate" (pronounced "kee-late") comes from the Greek word for "claw." The process of chelation "claws" onto a mineral, protecting it and making it far easier for your body to absorb.
Chelation: Giving Minerals a "VIP Pass"
Think of your gut as a busy nightclub with a strict doorman. Standard minerals are like regular guests, stuck in a long line, competing to get in. A chelated mineral is like a guest with a VIP pass. It gets to bypass the line and walk right in, no questions asked.
How Amino Acids Protect and Escort Minerals
This VIP pass is an amino acid. In an amino acid chelate, the mineral is chemically bonded to one or more amino acids. This neutralizes the mineral's charge and tricks the body into thinking it's absorbing a protein. Our bodies are incredibly efficient at absorbing amino acids.
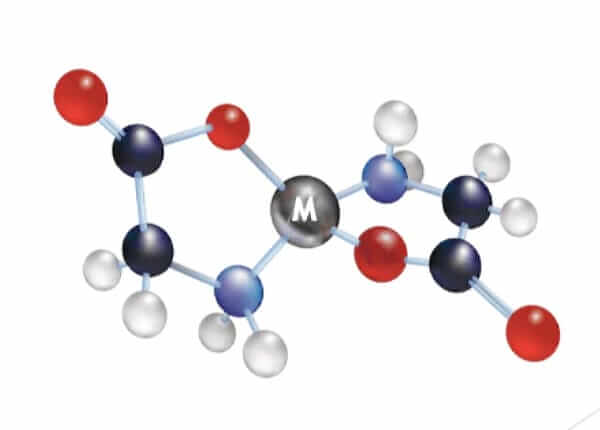
Bypassing the Traffic Jam for Direct Absorption
By hitching a ride with the amino acids, the mineral uses the body's highly efficient protein absorption pathways. This sophisticated system of nutrient transport avoids the competitive mineral absorption channels, leading to dramatically higher uptake.
The Top 3 Benefits of Choosing Chelated Minerals
This intelligent delivery system translates into three major advantages for your health and comfort. The primary benefits of chelated minerals are clear.
Benefit #1: Superior Bioavailability and Effectiveness
This is the number one reason to choose chelated minerals. Because more of the mineral is absorbed, more of it gets into your bloodstream to do its job—whether that's calming your nerves, supporting your immune system, or aiding muscle function. You get a more powerful effect from every dose.
Benefit #2: Enhanced Gentleness and Digestive Comfort
By preventing the mineral from causing irritation in the gut, chelation leads to significantly improved digestive comfort. This means you can take effective doses without the unwanted side effects, making chelated forms the ideal choice for those with sensitive stomachs.
Benefit #3: Greater Stability and Purity
The chelation process creates a very stable molecule that is less likely to react with other substances in the supplement or in your food. This ensures the purity and potency of the mineral, delivering a higher supplement quality from the bottle to your cells.
Common Types of Chelated Minerals to Look For
When you're reading a supplement label, it's helpful to recognize the names of common chelated forms.
Bisglycinates: The Gold Standard for Absorption and Gentleness
Minerals chelated with two glycine amino acids, like Magnesium Bisglycinate or a Zinc Bisglycinate supplement, are often considered the gold standard. They are known for being exceptionally well-absorbed and extremely gentle on the stomach.
Citrates and Malates: Other Effective Chelated Forms
Forms like citrates (bound to citric acid) and malates (bound to malic acid) are also considered chelated and offer good bioavailability, though bisglycinates are typically seen as the premium choice for both absorption and gentleness.
How to Identify Chelated Minerals on a Label
How do I know if a mineral is chelated? Look for names that end in "-ate" or include an amino acid name. For example, "Magnesium Bisglycinate," "Zinc Picolinate," or "as Magnesium Malate." The label should clearly state the form used. iMissoft is committed to using these superior forms in our mineral supplements.
Unlock the True Potential of Minerals with Chelation
Choosing a mineral supplement isn't just about the dosage on the front of the bottle. It's about the intelligence of the formula inside. Chelation is the key to unlocking the full power of these essential nutrients.
Key Takeaways: Don't Just Supplement, Absorb
- Standard mineral supplements often have poor absorption and can cause digestive issues.
- Chelated minerals use amino acids to create a "VIP pass" for superior mineral absorption.
- This leads to greater effectiveness, better digestive comfort, and higher overall quality.
A Call to Action: Upgrade to a Smarter Mineral Supplement
Stop wasting money on minerals your body can't use. Experience the difference in absorption and comfort with iMissoft's premium line of chelated minerals. Upgrade your supplement strategy today.
Your Questions About Chelation and Mineral Supplements
Are chelated minerals more expensive? Are chelated minerals worth the price? Initially, they may have a higher price point than basic mineral salts. However, when you factor in the vastly superior mineral bioavailability (meaning less is wasted), the cost per effective, absorbed milligram is often much lower. You are paying for results, not for waste.
Are chelated minerals safe? Yes, they are very safe. In fact, they are often considered safer than non-chelated forms because their gentleness on the digestive system reduces the risk of side effects. The amino acids used in chelation are natural and easily recognized by the body.
How do I know if a mineral supplement is truly chelated? A reputable brand will clearly state the specific chelated form on the "Supplement Facts" panel (e.g., "Magnesium as Magnesium Bisglycinate Chelate"). Be wary of vague terms like "amino acid blend." Transparency is a hallmark of a high-quality brand like iMissoft.
Can I get enough chelated minerals from food? Your body naturally chelates minerals from the food you eat during digestion. However, modern diets and soil depletion mean many people don't get optimal levels. For those needing extra support, a high-quality chelated supplement is the most direct and effective way to ensure adequate intake.